Lab presentation
The connections in our brains are constantly changing. As we interact with the environment and with each other, connections between our neurons are remodeled so that we can retain these interactions as learning and memory. At a molecular level, the brain accomplishes this remodeling in part by making new proteins at the specific sites where our neurons interact with each other (known as synapses). Abnormalities in synaptic plasticity contribute to a wide range of neurological and cognitive disorders, such as schizophrenia, autism, addiction and multiple sclerosis. The goal of our research is to understand the molecular and cellular mechanisms involved in synaptic plasticity and the remodeling of the neuronal connectome. We use a multidisciplinary experimental approach that includes high-resolution live imaging of neurons, gene manipulation, electrophysiology and multi-omics studies.
Projects
SYNAPTIC PLASTICITY and mRNA CONDENSATES IN SCHIZOPHRENIA
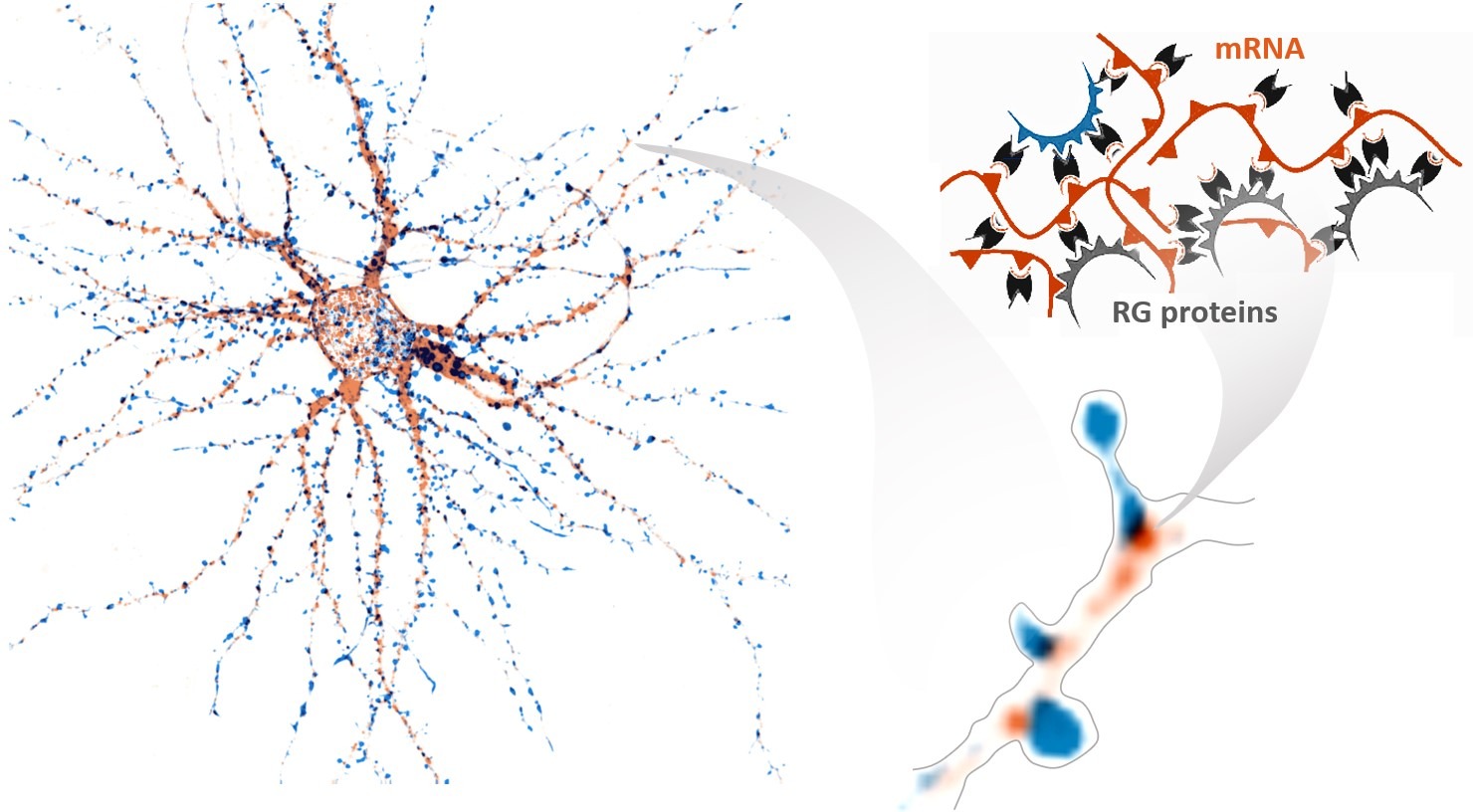
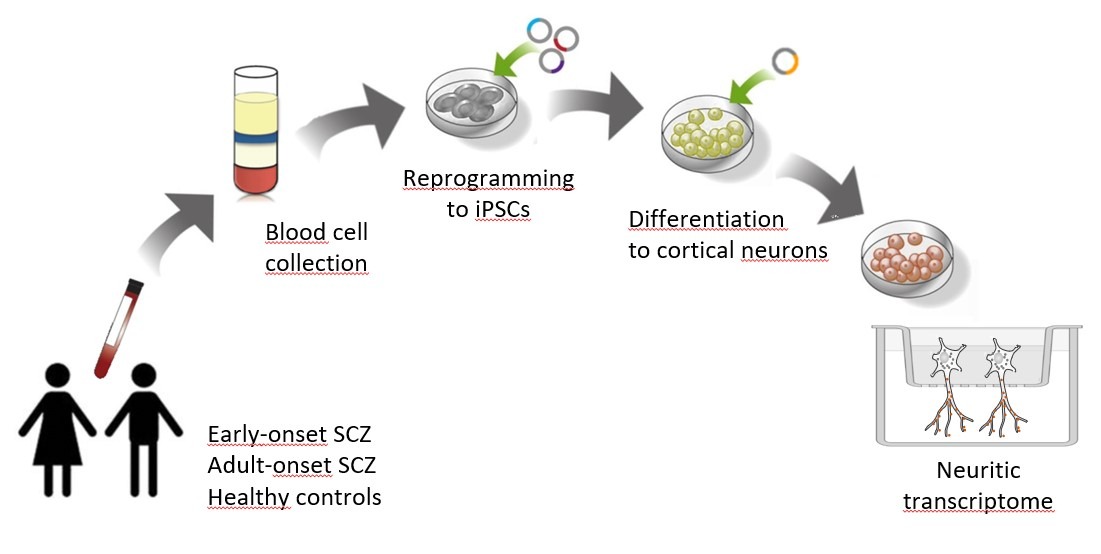
Schizophrenia (SCZ) is a brain disease that affects how a person thinks, feels, and behaves. Evidence indicates that many aspects of the clinical manifestation of SCZ are due to alterations in synaptic function, which depends on the localization of mRNAs at synapses for local protein synthesis. Moreover, the assembly of mRNAs into RNA condensates has emerged as an important mechanism underlying RNA trafficking in neurites. However, the molecular mechanisms that drive these processes and their relation to synaptic dysfunction are mostly unknown. We hypothesize that genomic/transcriptomic variability, by causing imbalanced mRNA condensation and transport to the synapses, underlies synaptic connectivity defects in SCZ and, therefore, is associated with the risk for the disorder in distinct clinical and neurobiological subgroups. The main goal of this project is to advance into the identification of molecular and cellular mechanisms underlying the pathophysiology of SCZ, as an essential step in identifying prediction markers and developing new treatments.
SYNAPTIC CAPTURE of RNA GRANULES and NEURONAL PLASTICITY
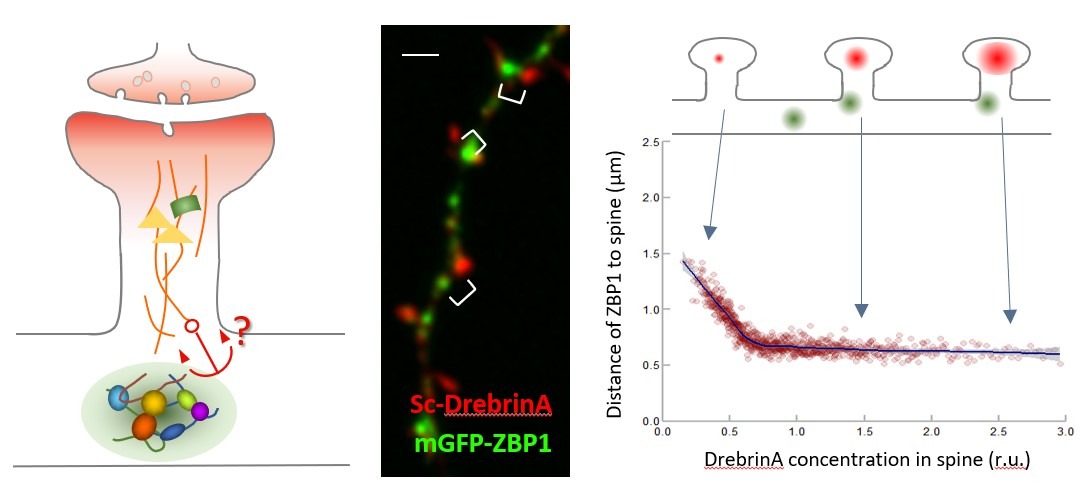
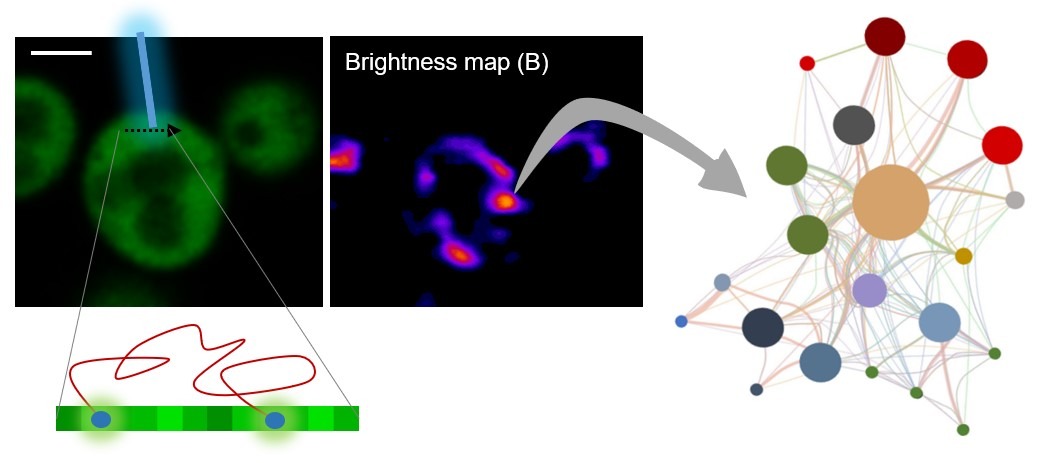
Neurons, above all other cell types, need to transport mRNAs at very long distances to fuel local translation in synapses and allow efficient, spatially localized, and specific remodeling of synapses by external stimuli. To translocate from the cell body to a distant site in the neurites, mRNA molecules assemble with proteins into RNA granules, which display constitutive bidirectional movement along axons and dendrites. The main purpose of this project is to study the molecular mechanisms that drive and regulate RNA granule capture at synapses in the context of neuronal plasticity, aiming at a better understanding of the relationship between RNA granule dynamics, dendritic spine remodeling and synaptic activity, which are thought to be key factors for memory formation. We expect to provide a molecular framework to the long-sought mechanisms maintaining synaptic strength in neurons and, hence, foster our knowledge on memory formation at the molecular level.
ANTIPRIONS: FUNCTIONAL VARIOMICS to TACKLE NEUROPATHOLOGICAL PROTEIN AGGREGATION
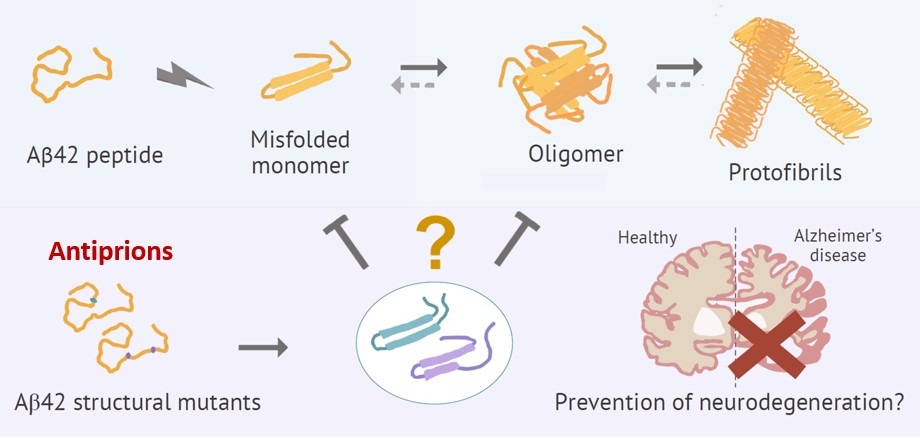
Prion-like aggregation has been directly implicated in neurodegenerative pathologies such as Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s and Huntington’s diseases, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. However, appropriate therapeutic approaches and effective treatments are largely lacking. Here we hypothesize that, similarly to the opposing twins Prometheus and Epimetheus, antiprions can be created from prion domains as quasi-twin structures that still bind with high efficiency to prion aggregates but do not transmit the pathological fold to newly recruited monomers, thus arresting prion aggregate growth. We are currently using Aβ42, αSyn and TDP-43 as initials seeds to perform extensive and highly-sensitive variomic screens under orthogonal selection scenarios, and comprehensive functional assays of the isolated antiprions to validate their ability to counteract prion-like aggregation and deleterious effects in neurons. If successful, our work will constitute the foundational basis of preclinical and clinical assays directed to test and refine their use in major neurodegenerative diseases.
PROTEIN FLOCKS and NETWORK CHANNELING
Whether sequential metabolic reactions and other complex step-wise intracellular processes are efficiently executed by proteins dispersed in a crowded environment is a matter of debate. On the other hand, the existence of stable interactions holding a large number of proteins all together in a keylock manner to perform a set of complex sequential reactions or processes is rather exceptional. Based on our previous work on single-molecule dynamics of two major yeast chaperones, we are testing the hypothesis that functional channeling in protein networks could be driven by very transient interactions within protein flocks, well beyond those of membrane-less organelles. We are currently using single-molecule fluctuation analysis and high-throughput proximity-labeling methods to analyze the specificity and composition of the identified protein flocks. Finally, we will use the armamentarium of molecular and cellular biology tools offered by the budding yeast to study the relevance of flock identity in the efficiency of paradigmatic pathways and networks.
Lab people

Carme Gallego

Martí Aldea
Principal investigator
After receiving the Ph.D. degree in Biological Sciences in 1989 under the supervision of Dr. Josep Carreras (University of Barcelona), she did postdoctoral work with Dr. Gary Johnson at the National Jewish Center Hospital (Denver, Co, USA), studying the molecular mechanisms of cell malignancy in cancerous cells. The most significant contribution from this postdoctoral period was to the study of the inhibitory G protein α subunit (Gi α) as an oncogenic protein and its role in controlling specific MAPK pathways. In 1992 she joined the University of Lleida first as postdoctoral fellow and later as research associate to work in collaboration with Dr. Martí Aldea on the molecular mechanisms that control the earliest steps of the cell cycle in budding yeast. In 2000 she obtained a permanent position as Associated Professor starting her career as principal investigator in the field of molecular neuroscience. In September 2010 she joined the IBMB-CSIC as a Research Scientist and recently she has been promoted to Senior Research Scientist. Her research is aimed at understanding the cellular and molecular mechanisms involved in the regulation of synaptic plasticity and memory formation. Her group is interested in how the transport and local expression of mRNAs encoding synaptic proteins are regulated and how these mechanisms in response to activity affect synapse development and plasticity. In particular, they are studying the molecular mechanisms whose dysfunction produces alterations in synaptic function causing mental disorders such as schizophrenia or autism.
Principal investigator
After receiving the Ph.D. degree in Biological Sciences from the Autonomous University of Barcelona, he did postdoctoral work with Dr. Miguel Vicente at the Center of Biological Research (CSIC, Madrid) and with Dr. Sidney Kushner at the University of Georgia (USA), trying to understand the mechanisms that coordinate growth and cell division in Escherichia coli. After joining the University of Lleida he initiated his career as an independent scientist focusing on the control of the earliest steps of the cell cycle. During this period, his group discovered and deeply characterized two post-transcriptional mechanisms that control expression and localization of the yeast G1 cyclin. Later work at the IBMB lead him to identify a molecular switch for cell cycle entry, unveiling an unexpected link between protein aggregation and cell cycle entry that sets proteostasis decline as a key factor causing cell proliferation decay during aging. His group also uncovered a timer mechanism that modulates G1 length to preserve a fraction of slow growing cells within the population. As a result of the most recent work, his research team has showed that yeast and mouse cells maintain their size within narrow limits to obtain a properly balanced transcriptome and, as a result, maximize growth and fitness during proliferation.

Galal Yahya A. Metwally

Blanca Poquet

Kanad Roy

Kimberly Alomoto

Linda Luna Iturra
Past students
Neus Pedraza
Eva Parisi
Maya V Georgieva
Francisco Ferrezuelo
Eloi Garí
Mónica Mendoza
Alexis Pérez
Marcos Moreno
Joan M Martínez-Láinez
Sara Gutiérrez
Pedro J Vidal
David F Moreno
Raül Ortiz
Marta Rafel
Maria Ruiz-Miró
Serafí Cambray
Emili Vergés
Yuhui Liu
Hongyin Wang
Neus Colomina
Selected publications
Vidal PJ, Pérez AP, Yahya G, Aldea M. (2024) Transcriptomic balance and optimal growth are determined by cell size. Molecular Cell 84 doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2024.07.005
Moreno-Aguilera M, Neher AM, Mendoza MB, Dodel M, Mardakheh FK, Ortiz R, Gallego C (2024) KIS counteracts PTBP2 and regulates alternative exon usage in neurons. eLife 13 doi: 10.7554/eLife.96048
Pérez AP, Artés MH, Moreno DF, Clotet J, Aldea M (2022) Mad3 modulates the G1 Cdk and acts as a timer in the Start network. Science Advances 8 doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abm4086
Yahya G, Pérez AP, Mendoza MB, Parisi E, Moreno DF, Artés MH, Gallego C, Aldea M (2021) Stress granules display bistable dynamics modulated by Cdk. Journal of Cell Biology 220 doi: 10.1083/jcb.202005102
Mendoza MB, Gutierrez S, Ortiz R, Moreno DF, Dermit M, Dodel M, Rebollo E, Bosch M, Mardakheh FK, Gallego C (2021) eEF1A2 controls translation and actin dynamics in dendritic spines. Science Signaling 14 doi: 10.1126/scisignal.abf5594
Moreno DF, Jenkins K, Morlot S, Charvin G, Csikasz-Nagy A, Aldea M (2019) Proteostasis collapse, a hallmark of aging, hinders the chaperone-Start network and arrests cells in G1. eLife 8 doi: 10.7554/eLife.48240
Martínez-Láinez JM, Moreno DF, Parisi E, Clotet J, Aldea M (2018) Centromeric signaling proteins boost G1 cyclin degradation and modulate cell size in budding yeast. PLoS Biology 16 doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.2005388
Parisi E, Yahya G, Flores A, Aldea M (2018) Cdc48/p97 segregase is modulated by Cdk to determine cyclin fate during G1 progression. The EMBO Journal 37 doi: 10.15252/embj.201798724
Ortiz R, Georgieva MV, Gutierrez S, Pedraza N, Fernandez-Moya SM, Gallego C (2017) Recruitment of Staufen2 enhances dendritic localization of an intron-containing CaMKIIα mRNA. Cell Reports 20 doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.06.026
Georgieva MV, Yahya G, Codó L, Ortiz R, Teixidó L, …, Gelpí JL, Gallego C, Orozco M, Aldea (2015) Inntags: small self-structured epitopes for innocuous protein tagging. Nature Methods 12 doi: 10.1038/nmeth.3556
Yahya G, Parisi E, Flores A, Gallego C, Aldea M (2014) A Whi7-anchored loop controls de G1 Cdk-cyclin complex at Start. Molecular Cell 53 doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2013.11.015
Pedraza, N., Ortíz, R., Cornadó, A., Llobet, A., Aldea, M., and Gallego, C (2014) KIS, a kinase associated with microtubule regulators, enhances translation of AMPA receptors and stimulates dendritic spine remodeling. Journal of Neuroscience 34 doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1573-14.2014
Ferrezuelo F, Colomina N, Palmisano A, Garí E, Gallego C, Csikasz-Nagy A, Aldea M (2012) The critical size is set at a single-cell level by growth rate to attain homeostasis and adaptation. Nature Communications 3 doi: 10.1038/ncomms2015
Ferrezuelo F, Colomina N, Futcher B, Aldea M (2010) The transcriptional network activated by Cln3 cyclin at the G1-to-S transition of the yeast cell cycle. Genome Biology 11 doi: 10.1186/gb-2010-11-6-r67
Vergés E, Colomina N, Garí E, Gallego C, Aldea M (2007) Cyclin Cln3 is retained at the ER and released by the J-chaperone Ydj1 in late G1 to trigger cell cycle entry. Molecular Cell 26 doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2007.04.023
Wang H, Garí E, Vergés E, Gallego C, Aldea M (2004) Recruitment of Cdc28 by Whi3 restricts nuclear accumulation of the G1 cyclin-Cdk complex to late G1. The EMBO Journal 23 doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600022
Garí E, Volpe T, Wang H, Gallego C, Futcher B, Aldea M (2001) Whi3 binds the mRNA of the G1 cyclin CLN3 to modulate cell fate in budding yeast. Genes & Development 15 doi: 10.1101/gad.203501
Colomina N, Garí E, Gallego C, Herrero E, Aldea M (1999) G1 cyclins block the Ime1 pathway to make mitosis and meiosis incompatible in budding yeast. The EMBO Journal 18 doi: 10.1093/emboj/18.2.320
Gallego C, Garí E, Colomina N, Herrero E, Aldea M (1997) The Cln3 cyclin is downregulated by translational repression and degradation during the G1 arrest caused by nitrogen deprivation in budding yeast. The EMBO Journal 16 doi: 10.1093/emboj/16.23.7196
All publications
Vidal PJ, Pérez AP, Yahya G, Aldea M. (2024) Transcriptomic balance and optimal growth are determined by cell size. Molecular Cell 84 doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2024.07.005
Moreno-Aguilera M, Neher AM, Mendoza MB, Dodel M, Mardakheh FK, Ortiz R, Gallego C (2024) KIS counteracts PTBP2 and regulates alternative exon usage in neurons. eLife 13 doi: 10.7554/eLife.96048
Almodóvar-Payá C, Guardiola-Ripoll M, Giralt-López M, Oscoz-Irurozqui M, Canales-Rodríguez EJ, Madre M……, Gallego C, Pomarol-Clotet E, Fatjó-Vilas M (2024) NRN1 epistasis with BDNF and CACNA1C: mediation effects on symptom severity through neuroanatomical changes in schizophrenia. Brain Struct Funct 9 doi: 10.1007/s00429-024-02793-5
Pérez AP, Artés MH, Moreno DF, Clotet J, Aldea M (2022) Mad3 modulates the G1 Cdk and acts as a timer in the Start network. Science Advances 8 doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abm4086
Almodóvar-Payá C, Guardiola-Ripoll M, Giralt-López M, Gallego C, ……., Pomarol-Clotet E, Fatjó-Vilas M (2022) NRN1 Gene as a Potential Marker of Early-Onset Schizophrenia: Evidence from Genetic and Neuroimaging Approaches. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23 doi: 10.3390/ijms23137456
Yahya G, Pérez AP, Mendoza MB, Parisi E, Moreno DF, Artés MH, Gallego C, Aldea M (2021) Stress granules display bistable dynamics modulated by Cdk. Journal of Cell Biology 220 doi: 10.1083/jcb.202005102
Mendoza MB, Gutierrez S, Ortiz R, Moreno DF, Dermit M, Dodel M, Rebollo E, Bosch M, Mardakheh FK, Gallego C (2021) eEF1A2 controls translation and actin dynamics in dendritic spines. Science Signaling 14 doi: 10.1126/scisignal.abf5594
Moreno DF, Jenkins K, Morlot S, Charvin G, Csikasz-Nagy A, Aldea M (2019) Proteostasis collapse, a hallmark of aging, hinders the chaperone-Start network and arrests cells in G1. eLife 8 doi: 10.7554/eLife.48240
Moreno DF, Parisi E, Yahya G, Vaggi F, Csikász-Nagy A, Aldea M (2019) Competition in the chaperone-client network subordinates cell-cycle entry to growth and stress. Life Science Alliance 2 doi: 10.26508/lsa.201800277
Moreno DF, Aldea M (2019) Coincidence analysis of molecular dynamics by raster-image correlation spectroscopy. Methods in Molecular Biology 2040 doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-9686-5_17
Martínez-Láinez JM, Moreno DF, Parisi E, Clotet J, Aldea M (2018) Centromeric signaling proteins boost G1 cyclin degradation and modulate cell size in budding yeast. PLoS Biology 16 doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.2005388
Parisi E, Yahya G, Flores A, Aldea M (2018) Cdc48/p97 segregase is modulated by Cdk to determine cyclin fate during G1 progression. The EMBO Journal 37 doi: 10.15252/embj.201798724
Saarikanga J, Caudron F, Prasad R, Moreno DF, Bolognesi A, Aldea M, Barral Y (2017) Compartmentalization of ER-bound chaperone confines protein deposit formation to the aging yeast cell. Current Biology 27 doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2017.01.069
Ortiz R, Georgieva MV, Gutierrez S, Pedraza N, Fernandez-Moya SM, Gallego C (2017) Recruitment of Staufen2 enhances dendritic localization of an intron-containing CaMKIIα mRNA. Cell Reports 20 doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.06.026
Aldea M, Jenkins K, Csikász-Nagy (2017) Growth Rate as a Direct Regulator of the Start Network to Set Cell Size. Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology 5 doi: 10.3389/fcell.2017.00057
Asensio-Juan E, Fueyo R, Pappa S, Iacobucci S, Badosa C, Lois S, Balada M, Bosch-Presegué L, Vaquero A, Gutiérrez S, Caelles C, Gallego C, de la Cruz X, Martínez-Balbás MA (2017) The histone demethylase PHF8 is a molecular safeguard of the IFNγ response. Nucleic Acids Research 45 doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw1346
Muñoz-Cobo JP, Sánchez-Hernández N, Gutiérrez S, El Yousfi Y, Montes M, Gallego C, Hernández-Munain C, Suñé C (2017) Transcriptional Elongation Regulator 1 Affects Transcription and Splicing of Genes Associated with Cellular Morphology and Cytoskeleton Dynamics and Is Required for Neurite Outgrowth in Neuroblastoma Cells and Primary Neuronal Cultures. Molecular Neurobiology 54 doi: 10.1007/s12035-016-0284-6
Deniz Ö, Flores O, Aldea M, Soler-López M, Orozco M (2016) Nucleosome architecture throughout the cell cycle. Scientific Reports 6 doi: 10.1038/srep19729
Georgieva MV, Yahya G, Codó L, Ortiz R, Teixidó L, …, Gelpí JL, Gallego C, Orozco M, Aldea (2015) Inntags: small self-structured epitopes for innocuous protein tagging. Nature Methods 12 doi: 10.1038/nmeth.3556
Yahya G, Parisi E, Flores A, Gallego C, Aldea M (2014) A Whi7-anchored loop controls de G1 Cdk-cyclin complex at Start. Molecular Cell 53 doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2013.11.015
Pedraza N, Ortiz R, Cornado A, Llobet A, Aldea M, Gallego C (2014) KIS, a kinase associated with microtubule regulators, enhances translation of AMPA receptors and stimulates dendritic spine remodeling. Journal of Neuroscience 34 doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1573-14.2014
Menoyo S, Ricco N, Bru S, Hernández-Ortega S, Escoté X, Aldea M, Clotet J (2013) Phosphate-activated CDK stabilizes G1 cyclin to trigger cell cycle entry. Molecular and Cellular Biology 33 doi: 10.1128/MCB.01556-12
Ferrezuelo F, Colomina N, Palmisano A, Garí E, Gallego C, Csikasz-Nagy A, Aldea M (2012) The critical size is set at a single-cell level by growth rate to attain homeostasis and adaptation. Nature Communications 3 doi: 10.1038/ncomms2015
Asensio-Juan E, Gallego C, Martínez-Balbás MA (2012) The histone demethylase PHF8 is essential for cytoskeleton dynamics. Nucleic Acids Research 40 doi: 10.1093/nar/gks716. Epub 2012 Jul 31
Baba M, Keller JR, Sun HW, Resch W, Kuchen S, Suh HC, Hasumi H, Hasumi Y, Kieffer-Kwon KR, Gallego C,…, Linehan WM, Casellas R (2012) The Folliculin-Fnip1 pathway deleted in human Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome is required for B cell development. Blood 120 doi: 10.1182/blood-2012-02-410407
Fernández RMH, Ruiz-Miró M, Dolcet X, Aldea M, Garí E (2011) Cyclin D1 interacts and collaborates with Ral GTPases enhancing cell detachment and motility. Oncogene 30 doi: 10.1038/onc.2010.577
Ruiz-Miro M, Colomina N, Fernandez RMH, Gari E, Gallego C, Aldea M (2011) Translokin (Cep57) interacts with cyclin D1 and prevents its nuclear accumulation in quiescent fibroblasts. Traffic 12 doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2011.01176.x
Ferrezuelo F, Colomina N, Futcher B, Aldea M (2010) The transcriptional network activated by Cln3 cyclin at the G1-to-S transition of the yeast cell cycle. Genome Biology 11 doi: 10.1186/gb-2010-11-6-r67
Cardus A, Panizo S, Encinas M, Dolcet X, Gallego C, Aldea M, Fernández E, Valdivielso JM (2009) 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D(3) regulates VEGF production through a vitamin D response element in the VEGF promoter. Atherosclerosis 204 doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2008.08.020
Ferrezuelo F, Aldea M, Futcher B (2009) Bck2 is a phase-independent activator of cell cycle-regulated genes in yeast. Cell Cycle 8 doi: 10.4161/cc.8.2.7543
Pedraza N, Rafel M, Navarro I, Encinas M, Aldea M, Gallego C (2009) Mixed lineage kinase phosphorylates transcription factor E47 and inhibits TrkB expression to link neuronal death and survival pathways. Journal of Biological Chemistry 284 doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.038729
Cambray S, Pedraza N, Rafel M, Gari E, Aldea M, Gallego C (2009) Protein kinase KIS localizes to RNA granules and enhances local translation. Molecular and Cellular Biology 29 doi: 10.1128/MCB.01180-08
Colomina N, Ferrezuelo F, Verges E, Aldea M, Gari E (2009) Whi3 regulates morphogenesis in budding yeast by enhancing Cdk functions in apical growth. Cell Cycle 8 doi: 10.4161/cc.8.12.8740
Colomina N, Ferrezuelo F, Wang H, Aldea M, Gari E (2008) Whi3, a developmental regulator of budding yeast, binds a large set of mRNAs functionally related to the endoplasmic reticulum. Journal of Biological Chemistry 283 doi: 10.1074/jbc.M804604200
Aldea M, Gari E, Colomina N (2007) Control of cell cycle and cell growth by molecular chaperones. Cell Cycle 6 doi: 10.4161/cc.6.21.4920
Vergés E, Colomina N, Garí E, Gallego C, Aldea M (2007). Cyclin Cln3 is retained at the ER and released by the J-chaperone Ydj1 in late G1 to trigger cell cycle entry. Molecular Cell 26 doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2007.04.023
Cardús A, Parisi E, Gallego C, Aldea M, Fernández E, Valdivielso JM (2006) 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 stimulates vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation through a VEGF-mediated pathway. Kidney International 69 doi: 10.1038/sj.ki.5000304
Clotet J, Escoté X, Adrover MA, Garí E, Aldea M, De Nadal E, Posas F (2006). Phosphorylation of Hsl1 by Hog1 leads to a G2 arrest essential for cell survival at high osmolarity. The EMBO Journal 25 doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601095
Liu YH, Encinas M, Comella JX, Aldea M, Gallego C (2004) Basic helix-loop-helix proteins bind to TrkB and p21(Cip1) promoters linking differentiation and cell cycle arrest in neuroblastoma cells. Molecular and Cellular Biology 24 doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.7.2662-2672.2004
Wang H, Garí E, Vergés E, Gallego C, Aldea M (2004). Recruitment of Cdc28 by Whi3 restricts nuclear accumulation of the G1 cyclin-Cdk complex to late G1. The EMBO Journal 23 doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600022
Sole C, Dolcet X, Segura MF, Gutierrez H, Diaz-Meco MT, Gozzelino R, Sanchis D, Bayascas JR, Gallego C, Moscat J, Davies AM, Comella JX (2004) The death receptor antagonist FAIM promotes neurite outgrowth by a mechanism that depends on ERK and NF-κB signalling. Journal of Cell Biology 167 doi: 10.1083/jcb.200403093
Colomina N, Liu YH, Aldea M, Gari E (2003) TOR regulates the subcellular localization of Ime1, a transcriptional activator of meiotic development in budding yeast. Molecular and Cellular Biology 23 doi: 10.1128/MCB.23.20.7415-7424.2003
Ferrezuelo F, Steiner B, Aldea M, Futcher B (2002) Biogenesis of yeast telomerase depends on the importin Mtr10. Molecular and Cellular Biology 22 doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.17.6046-6055.2002
Belli G, Gari E, Aldea M, Herrero E (2001) Osmotic stress causes a G(1) cell cycle delay and downregulation of Cln3/Cdc28 activity in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Molecular Microbiology 39 doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2001.02297.x
Garí E, Volpe T, Wang H, Gallego C, Futcher B, Aldea M (2001). Whi3 binds the mRNA of the G1 cyclin CLN3 to modulate cell fate in budding yeast. Genes & Development 15 doi: 10.1101/gad.203501
Encinas M, Iglesias M, Liu Y, Wang H, Muhaisen A, Ceña V, Gallego C, Comella JX (2000) Sequential treatment of SH-SY5Y cells with retinoic acid and brain-derived neurotrophic factor gives rise to fully differentiated, neurotrophic factor-dependent, human neuron-like cells. Journal of Neurochemistry 75 doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.2000.0750991.x
Colomina N, Garí E, Gallego C, Herrero E, Aldea M (1999). G1 cyclins block the Ime1 pathway to make mitosis and meiosis incompatible in budding yeast. The EMBO Journal 18 doi: 10.1093/emboj/18.2.320
Clotet J, Gari E, Aldea M, Arino J (1999) The yeast Ser/Thr phosphatases Sit4 and Ppz1 play opposite roles in regulation of the cell cycle. Molecular and Cellular Biology 19 doi: 10.1128/MCB.19.3.2408
Belli G, Gari E, Piedrafita L, Aldea N, Herrero E (1998) An activator/repressor dual system allows tight tetracycline-regulated gene expression in budding yeast. Nucleic Acids Research 26 doi: 10.1093/nar/26.4.942
Wang RF, O’Hara EB, Aldea M, Bargmann CI, Gromley H, Kushner SR (1998) Escherichia coli mrsC is an allele of hflB, encoding a membrane-associated ATPase and protease that is required for mRNA decay. Journal of Bacteriology 180: doi: 10.1128/JB.180.7.1929-1938.1998
Colomina N, Aldea M (1998) Lumi-imagine! direct quantification of chemiluminescent signals Biochemica 1: 21
Belli G, Gari E, Aldea M, Herrero E (1998) Functional analysis of yeast essential genes using a promoter-substitution cassette and the tetracycline-regulatable dual expression system. Yeast 14 doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0061(19980915)14:12<1127::AID-YEA300>3.0.CO;2-%23
Gari E, Piedrafita L, Aldea M, Herrero E (1997) A set of vectors with a tetracycline-regulatable promoter system for modulated gene expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast 13 doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0061(199707)13:9<837::AID-YEA145>3.0.CO;2-T
Nadal A, Jares P, Cazorla M, Fernandez PL, Sanjuan X, Hernandez L, Pinyol M, Aldea M, Mallofre C, Muntane J, Traserra J, Campo E, Cardesa A (1997) p21(WAF1/Cip1) expression is associated with cell differentiation but not with p53 mutations in squamous cell carcinomas of the larynx. The Journal of Pathology 183 doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9896(199710)183:2<156::AID-PATH908>3.0.CO;2-O
Casas C, Aldea M, Espinet C, Gallego C, Gil R, Herrero E (1997) The AFT1 transcriptional factor is differentially required for expression of high-affinity iron uptake genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast 13 doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0061(19970615)13:7<621::AID-YEA121>3.0.CO;2-U
Gallego C, Garí E, Colomina N, Herrero E, Aldea M (1997). The Cln3 cyclin is downregulated by translational repression and degradation during the G1 arrest caused by nitrogen deprivation in budding yeast. The EMBO Journal 16 doi: 10.1093/emboj/16.23.7196
Dujon B, Albermann K, Aldea M, Alexandraki D, Ansorge W, et al (1997). The nucleotide sequence of Saccharomyces cerevisiae chromosome XV. Nature 387(Suppl.) doi: 10.1038/387s098
Gamo FJ, Lafuente MJ, Casamayor A, Arino J, Aldea M, Casas C, Herrero E, Gancedo C (1996) Analysis of the DNA sequence of a 15.5 kbp fragment near the left telomere of chromosome XV from Saccharomyces cerevisiae reveals a putative sugar transporter, a carboxypeptidase homologue and two new open reading frames. Yeast 12 doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0061(19960615)12:7%3C709::AID-YEA957%3E3.0.CO;2-1
Aldea M, Piedrafita L, Casas C, Casamayor A, Khalid H, Balcells L, Arino J, Herrero E (1996) Sequence analysis of a 12.8 kbp fragment of the left arm of yeast chromosome XV containing a putative 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase gene, a gene for a possible glycolphospholipid-anchored surface protein and six other open reading frames. Yeast 12 (sup) doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0061(199609)12:10B<1053::AID-YEA993>3.0.CO;2-S
Casamayor A, Khalid H, Balcells L, Aldea M, Casas C, Herrero E, Gamo FJ, Lafuente MJ, Gancedo C, Arino J (1996) Sequence analysis of a 13.4 kbp fragment from the left arm of chromosome XV reveals a malate dehydrogenase gene, a putative Ser/Thr protein kinase, the ribosomal L25 gene and four new open reading frames. Yeast 12 (sup) doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0061(199609)12:10B<1013::AID-YEA980>3.0.CO;2-5
Espinet C, Delatorre MA, Aldea M, Herrero E (1995) An efficient method to isolate yeast genes causing overexpression mediated growth arrest. Yeast 11: 25–32 doi: 10.1002/yea.320110104
Casamayor A, Aldea M, Casas C, Herrero E, Gamo FJ, Lafuente MJ, Gancedo C, Arino J (1995) DNA-sequence analysis of a 13 kbp fragment of the left arm of yeast chromosome -XV containing 7 new open reading frames. Yeast 11 doi: 10.1002/yea.320111308
Casas C, Aldea M, Casamayor A, Lafuente MJ, Gamo FJ, Gancedo C, Arino J, Herrero E (1995) Sequence analysis of a 9873 bp fragment of the left arm of yeast chromosome XV that contains the ARG8 and CDC33 genes, a putative riboflavin synthase beta-chain gene, and 4 new open reading frames. Yeast 11 doi: 10.1002/yea.320111107
Gan K, Sankaran K, Williams MG, Aldea M, Rudd KE, Kushner SR, Wu HC (1995) The umpA gene of Escherichia coli encodes phosphatidylglycerol:prolipoprotein diacylglyceryl transferase (lgt) and regulates thymidylate synthase levels through translational coupling. Journal of Bacteriology 177 doi: 10.1128/jb.177.7.1879-1882.1995
Comella JX, Sanzrodriguez C, Aldea M, Esquerda JE (1994) Skeletal muscle-derived trophic factors prevent motoneurons from entering an active cell-death program in vitro. Journal of Neuroscience 14 doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.14-05-02674.1994
Aldea M, Garrido T, Tormo A (1993) Gearbox gene expression and growth rate. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology 9 doi: 10.1007/BF00328029
Garrido T, Sanchez M, Palacios P, Aldea M, Vicente M (1993) Transcription of ftsZ oscillates during the cell cycle of Escherichia coli. The EMBO Journal 12 doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06073.x
Gallego C, Casas C, Herrero E (1993) Increased transformation levels in intact cells of Saccharomyces cerevisiae aculeacin A-resistant mutants Yeast 9 doi: 10.1002/yea.320090508
Gallego C, Gupta SK, Heasley LE, Qian NX, Johnson GL (1992) Mitogen-activated protein kinase activation resulting from selective oncogene expression in NIH 3T3 and Rat 1a cells. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA 89 doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7355.
Gupta SK, Gallego C, Johnson GL. (1992) Mitogenic pathways regulated by G protein oncògenes Molecular Biology of the Cell 3 doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.1.123
Gallego C, Gupta SK, Winitz S, Eisfelder BJ, Johnson GL (1992) Myristoylation of the Gai2 polypeptide, a G protein a subunit, is required for its signaling and transformation funcions. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA 89 doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.20.9695
Gupta SK, Gallego C, Johnson GL, Heasley LE (1992) Map Kinase is constitutively activated in gip2 and src transformed Rat 1a fibroblasts. Journal of Biological Chemistry 267
Gupta SK, Gallego C, Lowndes JM, Pleiman CM, Sable C, Eisfelder BJ, Johnson GL (1992) Analysis of fibroblast transformation potencial of GTPase-deficient gip2 oncogenes Molecular and Cellular Biology 12 doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.1.190-197.1992
Vicente M, Aldea M, Sacristán A, Rohde C, Weihs V, Kracht M, van Asma F, Kampert E, Hughes V, Jones C (1992) A standardized format for handling data on plasmids, viruses and transposons: The PVT database format. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology 8: doi: 10.1007/BF01201952
Vicente M, Palacios P, Dopazo A, Garrido T, Pla J, Aldea M (1991) On the chronology and topography of bacterial cell division. Research in Microbiology 142 doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(91)90038-C
Pla J, Sanchez M, Palacios P, Vicente M, Aldea M (1991) Preferential cytoplasmic location of Ftsz, a protein essential for Escherichia coli septation. Molecular Microbiology 5 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb01915.x
Vicente M, Kushner SR, Garrido T, Aldea M (1991) The role of the gearbox in the transcription of essential genes. Molecular Microbiology 5 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb02137.x
Gallego C, Graña X, Carreras J (1991) Increase of 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate synthase/phosphatase during maturation of reticulocytes with high 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate content. Molecular Cell Biochemistry 102 doi: 10.1007/BF00234576
Aldea M, Garrido T, Pla J, Vicente M (1990) Division genes in Escherichia coli are expressed coordinately to cell septum requirements by gearbox promoters. The EMBO Journal 9 doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07592.x
Gallego C, Carreras J (1990) 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate, fructose 2,6-bisphosphate and 1,6-glucose bisphosphate during maturation of reticulocytes with low 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate content. Molecular Cell Biochemistry 99 doi: 10.1007/BF01261389
Aldea M, Garrido T, Hernandez-Chico C, Vicente M, Kushner SR (1989) Induction of a growth-phase-dependent promoter triggers transcription of bolA, an Escherichia coli morphogene. The EMBO Journal 8 doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08573.x
Hamilton CM, Aldea M, Washburn BK, Babitzke P, Kushner SR (1989) New method for generating deletions and gene replacements in Escherichia coli. Journal of Bacteriology 171 doi: 10.1128/jb.171.9.4617-4622.1989
Gallego C, Carreras J (1989) Fructose 2,6-bisphosphate and 1,6-glucose bisphosphate levels in erythrocytes with high and low 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate content during postnatal development. FEBS Letters 251 doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81431-0.
Aldea M, Kushner SR (1988) CLONING – a microcomputer program for cloning simulations. Gene 65 doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90422-2
Aldea M, Maples VF, Kushner SR (1988) Generation of a detailed physical and genetic map of the ilv-metE-udp region of the Escherichia coli chromosome. Journal of Molecular Biology 200 doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90533-5
Aldea M, Kushner SR (1988) Instructions for the CLONING program. Gene 65 doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90423-4
Aldea M, Hernandez-Chico C, de la Campa AG, Kushner SR, Vicente M (1988) Identification, cloning, and expression of bolA, an ftsZ-dependent morphogene of Escherichia coli. Journal of Bacteriology 170 doi: 10.1128/jb.170.11.5169-5176.1988
de la Campa AG, Aldea M, Hernández-Chico C, Tormo A, Vicente M (1988) Segregation of elongation potential in Escherichia coli mediated by the wee genetic system. Current Microbiology 17 doi: 10.1007/BF01570871
Aldea M, Claverie-Martin F, Diaz-Torres MR, Kushner SR (1988) Transcript mapping using S35 DNA probes, trichloroacetate solvent and dideoxy sequencing ladders – a rapid method for identification of transcriptional start points. Gene 65 doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90421-0
Dopazo A, Tormo A, Aldea M, Vicente M (1987) Structural inhibition and reactivation of Escherichia coli septation by elements of the SOS and TER pathways. Journal of Bacteriology 169 doi: 10.1128/jb.169.4.1772-1776.1987
Gallego C, Bartrons R, Carreras J (1987) Fructose 2,6-bisphosphate and 1,6-glucose bisphosphate in rabbit erythroid cells during differentiation. FEBS Letters 1, doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80213-2.
Carreras J, Bartrons R, Espinet C, Gallego C (1987) Fructose 2,6-bisphosphate and 1,6-glucose bisphosphate in avian and mammalian erythroid cells Biomedical Biochimica Acta 46.
Tormo A, Ayala JA, de Pedro MA, Aldea M, Vicente M (1986) Interaction of FtsA and PBP3 proteins in the Escherichia coli septum. Journal of Bacteriology 166 doi: 10.1128/jb.166.3.985-992.1986
de la Campa AG, Tormo A, Martinez-Salas E, Aldea M, Vicente M (1985) Cell length in a wee dnaA mutant of Escherichia coli. Journal of Bacteriology 164 doi: 10.1128/jb.164.1.487-489.1985
Tormo A, Dopazo A, Delacampa AG, Aldea M, Vicente M (1985) Coupling between DNA replication and cell division mediated by the FtsA protein in Escherichia coli, a pathway independent of the SOS response, the TER pathway. Journal of Bacteriology 164 doi: 10.1128/jb.164.2.950-953.1985
Herrero E, Aldea M, Ros J, Monfort JM, Guerrero R (1982) Regulación de la division celular en Salmonella typhimurium. En Jiménez-Sánchez, A. and R. Guerrero (Eds.), pp 265-283. Genética Molecular Bacteriana. Reverté. Barcelona
Herrero E, Aldea M, Guerrero R (1982) Ciclo celular en bacterias. I. Aspectos moleculares. En Jiménez-Sánchez, A. y R. Guerrero (Eds.), pp 173-207. Genética Molecular Bacteriana. Reverté. Barcelona
Aldea M, Herrero E, Trueba FJ (1982) Constancy of diameter through the cell cycle of Salmonella typhimurium LT2. Current Microbiology 7: 165–8 doi: 10.1007/BF01568969
Aldea M, Herrero E, Esteve MI, Guerrero R (1980) Surface density of major outer-membrane proteins in Salmonella-typhimurium in different growth-conditions. Journal of General Microbiology 120 doi: 10.1099/00221287-120-2-355
Project funding
Targeting mRNAs condensates in neurites for a better understanding of synaptic plasticity dysfunction in schizophrenia
Fundació La Marató 202213-30/31 Mar Fatjó-Vilas (PI1) and Carme Gallego (PI2) 2023-2025
Ultradynamic protein assemblies and network channeling
MICINN PID2022-141460NB-I00 Martí Aldea (PI) 2023-2025
Proyecto PID2022-141460NB-I00 financiado por:

RNA granules in neurons: Molecular mechanisms of local capture, dissociation and translation
MICINN PID2020-113231GB-I00 Carme Gallego (PI) 2021-2024.
Proyecto PID2020-113231GB-I00 financiado por:

Protein cluster dynamics and network channeling
MICINN PID2019-109638GB-I00 Martí Aldea (PI) 2020-2022
Proyecto PID2019-109638GB-I00 financiado por:

Antiprions: a screen for prion mutants interfering with endogenous prion aggregation
AEI (EXPLORA), BIO2017-91613-EXP Martí Aldea (PI) 2019-2020
Proyecto BIO2017-91613-EXP financiado por:

El factor de elongación eEF1A2: Un vínculo emergente entre plasticidad sináptica y enfermedades neurológicas
MINECO BFU2017-83375-R Carme Gallego (PI) 2018-2021
Proyecto BFU2017-83375-R financiado por:

Proteotoxic aggregates, chaperome alterations and cell proliferation decline during cell aging
MINECO, BFU2016-80234-R Martí Aldea (PI) 2017-2019
Proyecto BFU2016-80234-R financiado por:

Synaptic plasticity and age at onset of psychotic disorders: molecular analysis of Neuritin
Fundación Alicia Koplowitz (FAK2016) Carme Gallego (co-PI) 2016-2018.
Plasticidad sináptica y enfermedades neurológicas: la isoforma eEF1A2 del factor de elongación de cerebro.
MINECO BFU2014-52591-R Carme Gallego (PI) 2015-2017.
Prions and aggregons as inhibitors of Start: a path to cell ageing
MINECO. BFU2013-47710-R Martí Aldea (PI) 2014-2016
Mecanismos moleculares de la plasticidad neuronal: función de la quinasa KIS
MICINN BFU2011-25914 Carme Gallego (PI) 2012-2014
EpiTag: Development of new peptidic tags
MICINN IPT-010000-2010-019 Martí Aldea (PI) 2011-2013
Molecular competition and cell size control
MICINN BFU2010-20205/BFS Martí Aldea (PI) 2011-2013
Vacancies/Jobs
If you are interested in joining the lab as postdoc or PhD student please send us your CV and cover letter to Carme Gallego (cggbmc@ibmb.csic.es) or Martí Aldea (mambmc@ibmb.csic.es)